![[Full Guide] How to End All Tasks in Task Manager](https://cdn.techloris.com/app/uploads/2023/04/How-to-End-all-Tasks-in-Task-Manager.png)
[Full Guide] How to End All Tasks in Task Manager
Task Manager is a powerful tool that allows users to monitor and manage running applications and processes on their Windows computers. While it can be a useful tool for troubleshooting system issues and terminating unresponsive programs, it is important to know how to use it properly to avoid causing damage to your system.
One common task that users may need to perform is ending all tasks in Task Manager, either to free up system resources or to resolve issues with a frozen or unresponsive computer. This article will guide you through the steps necessary to safely and effectively end all tasks in Task Manager on your Windows operating system.
Advantages of Ending Windows Processes via Task Manager
- Can resolve frozen or unresponsive programs: If a program becomes unresponsive, you may be unable to close it normally. Ending the program’s task in Task Manager can help resolve the issue and allow you to continue using your computer.
- Can free up system resources: Some programs or processes can consume many system resources, slowing down your computer’s performance. Ending unnecessary tasks in Task Manager can free up resources and help improve system performance.
- Provides more control over running processes: With Task Manager, you have more control over the processes running on your computer. This can help you identify and terminate any processes causing issues or taking up unnecessary resources.
Understanding the Task Manager
Tabs
When you open the Task Manager, you’ll see several tabs that allow you to view and manage different aspects of your system’s performance.
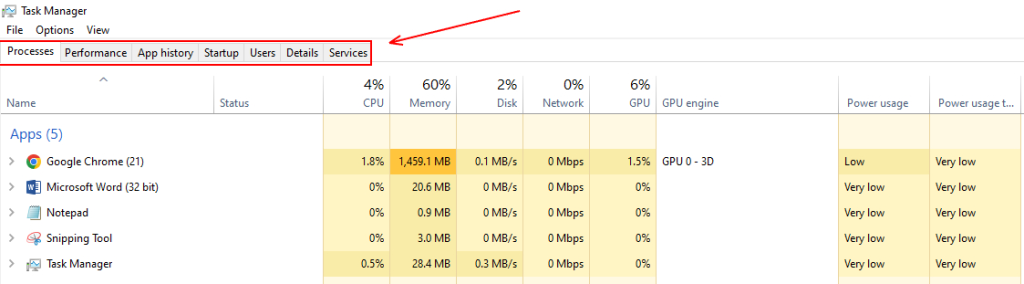
The Processes tab shows all the processes running on your system, including Windows processes, background processes, and any programs you have open. You can view information about the CPU, memory, disk, network, GPU, and another resource usage of each process. You can sort the list of processes by resource usage to identify which ones consume the most system resources. If you need to end a process, right-click on it and select “End task.” If you need to end all tasks in the Task Manager, you can right-click on any process and select “End task tree.”
The Performance tab provides real-time graphs showing the total resource usage for your system, including CPU, memory, disk, network, and GPU. You can use this tab to monitor your computer’s performance and identify any issues causing slowdowns or other problems.
The App History tab displays how much CPU and network resources apps have used for your current user account. This only applies to new Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps, such as those from the Microsoft Store, and not traditional Windows desktop apps (Win32 applications.)
The Startup tab lists your startup programs, and the Windows applications automatically start when you sign into your user account. You can disable startup programs from here to help speed up your computer’s startup time.
The Services tab allows you to manage system services, which are programs that run in the background and perform various control functions on your system. You can use this tab to start, stop, or disable services that may be causing issues on your computer.
The App History tab displays how much CPU and network resources apps have used for your current user account.
Zooming In on the Processes Tab
The processes tab in the Windows Task Manager displays all the running processes on your system, including system processes, Windows processes, and third-party software.
- Expand: Applications like Google Chrome have multiple processes grouped in the Processes tab. You can expand the process by clicking the arrow to its left or double-clicking on the process itself. This option is only available when you right-click on a group of processes.
- Collapse: Collapse an expanded group by clicking the arrow to its left.
- End task: End a process by right-clicking on it and selecting “End task.” You can also use the “End task” button at the list’s bottom.
- Restart: Restart Windows Explorer by right-clicking on it and selecting “Restart.” This option is only available for Windows Explorer.
- Resource values: View resource usage as a percentage or in precise values (such as MB) for memory, disk, and network usage.
- Create dump file: Capture a snapshot of a program’s memory and save it to disk for debugging purposes.
- Go to details: Go to the Details tab for more detailed technical information about a process.
- Open file location: Open File Explorer with the process’s .exe file selected by right-clicking on the process and selecting “Open file location.”
- Search online: Search for the name of a process on Bing by right-clicking on the process and selecting “Search online.”
- Properties: View the Properties window of the .exe file associated with the process by right-clicking on the process and selecting “Properties.”
How to Open Task Manager
To view and terminate processes that are using up a lot of resources, it is necessary to learn how to open Task Manager. There are several ways to do so:
- Right-click on the Taskbar and select Task Manager.
- Type “Task Manager” in the search bar on the Start menu and select the result.
- Use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Shift + Esc.
- Use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Alt + Del and select Task Manager.
- Use the keyboard shortcut Windows key + X to open the power-user menu and select Task Manager.
Identifying Processes With High-Resource Usage
Task Manager can diagnose issues when an application becomes unresponsive, a website takes an extended time to load, or when the system fan becomes loud. When examining the Processes tab, the initial step is to review the percentage of the total resource usage for the processor, memory, hard drive, and network. By clicking on the column names, you can sort the list and bring the ones consuming the most resources to the top. The issue might have been located if these resources were running high (90 percent or higher).
Stopping Processes With High-Resource Usage
Once you have identified the issue, you can terminate the process by right-clicking on it and selecting “End task.” Alternatively, you can select the item and click the “End task” button in the bottom-right corner.
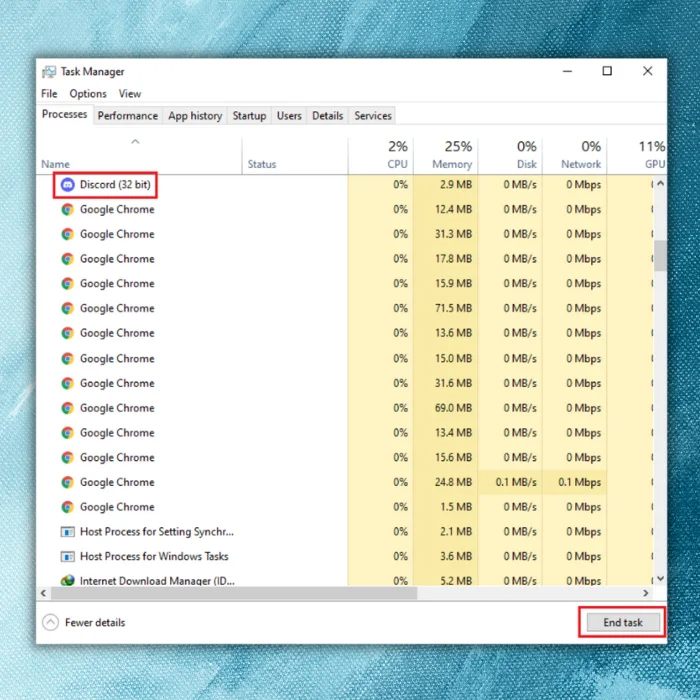
Other Ways to End Processes on Windows
Via the Command Prompt
Here are step-by-step instructions for opening the Command Prompt and terminating all processes on Windows:
- To open the Command Prompt, press the Windows key + R on your keyboard to bring up the Run dialog box.
2. Type “cmd” into the Run dialog box, press Enter or click OK.

3. To run Command Prompt with administrator privileges, press Ctrl + Shift + Enter. If prompted to allow changes to your device, click Yes.
4. In the Command Prompt window, type “taskkill /f /im ” and press Enter. This command will forcefully terminate all processes with a matching image name (process name) using the symbol to represent any process name.

5. Wait a few seconds while the command executes and terminates all the processes. This may take longer if many processes are running on your system.
6. Once the command has finished executing, all processes should be terminated. You can close the Command Prompt window by typing “exit” and pressing Enter or clicking the X button in the top right corner.
It is important to note that this command should only be used to terminate unresponsive processes and not misused for other purposes. The Command Prompt is a powerful tool in Windows and should be used cautiously.
Clean Boot Your Computer
1. Press the keyboard shortcut Windows + R, type “msconfig” into the Run dialog box, and hit Enter.
2. In the System Configuration pop up window, click on the “Services” tab.
3. Tick the box next to “Hide all Microsoft services” and click “Disable all”.

4. Next, go to the “Startup” tab and click “Open Task Manager”.

5. Select each startup item and click on “Disable”.
6. Once you’ve disabled all the startup items, close the Task Manager and restart your computer.
7. After your computer restarts, it will start with only a minimal set of drivers and programs. This can help to eliminate unnecessary processes and improve performance.
It’s important to note that this method should only be used to disable unnecessary processes and services. Disabling critical system processes or services can cause issues with your computer.
Using Powershell
1. To open PowerShell, press the keyboard shortcut Windows key + X and select “Windows PowerShell”.

2. In the PowerShell window, type the following command and hit Enter: “Get-Process | Stop-Process -Force”. This command will get a list of all processes and force them to stop.
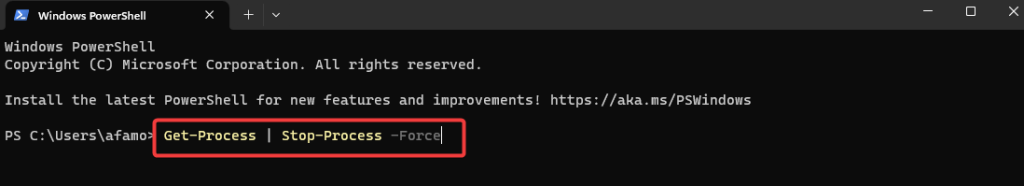
3. Wait a few seconds while the command executes and terminates all the processes.
It’s important to note that this command should only be used to terminate unresponsive processes and not misused for other purposes. PowerShell is a powerful tool in Windows and should be used with caution.
Force Quit Methods
Force Quit Using a Keyboard Shortcut
It is important to note that failing to complete the first step of this method will result in your computer shutting down instead of closing the application.
Here are the steps to follow:
- Choose the non-responsive application.
- Press the Alt + F4 keys together.
If your laptop doesn’t have function keys or the keyboard shortcut doesn’t work, you can use the Task Manager method instead.
Force Quit on Windows Using Command Prompt
The Command Prompt was a default app on older versions of Windows, but PowerShell has replaced it in recent versions. However, you can still use Command Prompt if you prefer it.
Here are the steps:
- Press Windows key + R.
2. Type cmd into the search box and press Enter.
3. Type tasklist and press Enter to display running programs and tasks.
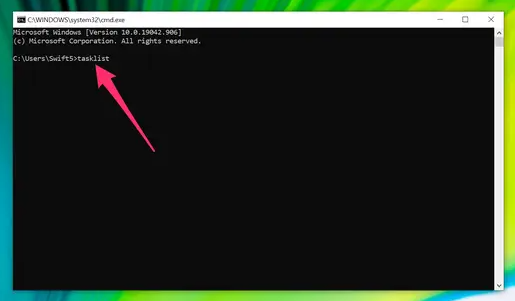
Screenshot of Command Prompt window on PC Type in “tasklist.” William Antonelli/Insider
- Enter taskkill /im [name_of_program].exe. For example, if you want to force quit Firefox, enter taskkill /im firefox.exe.
Screenshot of task kill code in Command Prompt screen To force quit an application like Firefox, this is what you’ll type in. William Antonelli/Insider
- Press Enter.
You’ll receive a confirmation message once the program is terminated.
Other Tools You Can Use to End All Windows Processes
CloseAll
If you prefer using third-party software to close running processes, CloseAll may be your best option. CloseAll automatically closes all processes with just a few clicks, bringing you back to your desktop. Some users recommend pinning CloseAll to the taskbar for quick access whenever needed. CloseAll can be downloaded for free from the official website.
Killer
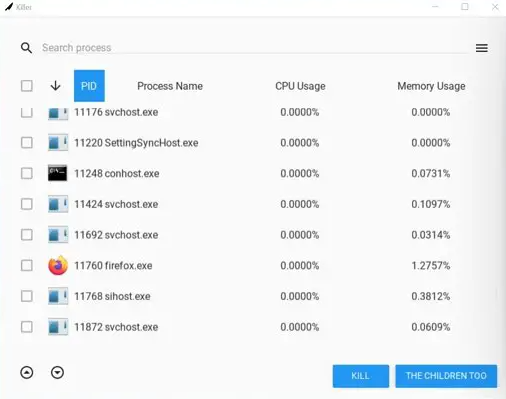
To begin, you must download and install the Killer app on your computer, which is readily available on Github.com. Once installed, launch the application by double-clicking on its icon on the desktop or using the Ctrl+Shift+K shortcut.
Once opened, locate the unresponsive or problematic process you want to terminate by checking the box beside it. You can kill a single task by clicking the “Kill” button at the bottom of the window or end all the tasks associated with the program by clicking “The Children Too.”
The Killer app is open-source, and its code is readily available online. This means you can trust the safety and security of the application without any concerns.
With the Killer app, you can quickly and efficiently end unresponsive or time-consuming tasks to terminate manually. The application occupies minimal hard drive space, and you don’t have to worry about it being a resource hog.
Following these steps, you can use the Killer app to terminate tasks on Windows 10, providing an alternative to the standard Task Manager.
Ultimate Process Killer
Ultimate Process Killer is a freeware tool that is portable and designed to scan the current processes running on a Windows computer along with its parent file path. With this tool, you can terminate a process and delete the originating file. It can also help you get rid of virus processes along with their parent virus files running in the background.
KillProcess

KillProcess is a free, portable application that can quickly terminate almost any process on a Windows computer, including services and system processes. You can select multiple processes by holding down the Ctrl key while selecting. This tool can even terminate protected Microsoft system processes, all within a matter of milliseconds.
Read: How to instantly terminate or kill all running processes or open applications.
Multi-Process Killer
Multi-Process Killer is an application that enables you to terminate multiple processes simultaneously by marking the checkboxes beside the desired processes and clicking the “kill selected processes” button.
Other Ways to Save Storage by Ending Background Processes
End ctfmon.exe
Task Manager’s Background Processes tab shows the ctfmon.exe process that runs in the background, and it’s responsible for providing alternative text input, like speech recognition and on-screen keyboards. You can safely end this task if you only use a mouse and keyboard and don’t require these additional input options.
End OneDrive.exe
Is OneDrive connected to your Windows account? It’s a popular program frequently included in the Office suite and pre-installed on your computer. This can save you some storage space, but if you prefer to back up your photos and videos independently, you can do so manually whenever you wish.
End LockApp.exe
The Windows lock screen control is not essential when your PC is active. You can terminate this process if you regularly turn off your computer after use and don’t need to worry about screen burn-in. It operates in the background and may consume some system resources.
Simplify Your Task Management: Mastering the Art of Ending Tasks in Task Manager
In this comprehensive guide, we explored the ins and outs of using Task Manager to end tasks in Windows. By understanding the various features and options available, you can effectively troubleshoot unresponsive applications and regain control over your system’s performance. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, mastering Task Manager empowers you to streamline your workflow and keep your computer running smoothly. With these valuable insights, you can confidently tackle any task-related issues that may arise, ensuring a seamless computing experience.

![[Windows Guide] How to Access Temp Files in Windows 10](https://cdn.techloris.com/app/uploads/2023/03/How-to-Access-Temp-Files-in-Windows-10.png)
![[2023] Upgrade Windows Using the Windows 10 Update Assistant](https://cdn.techloris.com/app/uploads/2023/04/Windows-10-Update-Assistant.png)

![[Full Guide] Turn Off UAC for One Program: Easy Guide](https://cdn.techloris.com/app/uploads/2023/03/disable-uac-for-one-program.png)