
Comprehensive Guide to Fixing the Blue Screen of Death Error
The Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) is a dark blue background error screen displayed by the Microsoft Windows operating system when it encounters a critical system error from which it cannot recover.
The BSOD typically indicates that the system has crashed and cannot continue running normally. The information displayed on the screen can provide important clues about the cause of the error, which can help diagnose and resolve the issue.
However, the BSOD can also indicate a serious problem that requires advanced technical expertise. In some cases, it may be necessary to reinstall the operating system or replace hardware components to restore normal system function.
What is the Main Cause of Blue Screen of Death?
The Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) can have many different causes, including hardware failures, driver issues, system failure software bugs, and system-level problems. The most common reasons for BSODs include faulty memory or storage devices, outdated or incompatible device drivers, corrupted system files, malware infections, and hardware overheating or power supply issues.
Other factors contributing to BSODs include system overclocking, improper software installation, and conflicts between software programs or system components. Identifying the root cause of a BSOD can often require advanced technical expertise and troubleshooting skills, as well as diagnostic tools and software.
How To Fix a ‘Blue Screen of Death on Your Windows Computer
The Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) is a dreaded error that many Windows users may encounter at some point in their computing experience. It usually appears as an intimidating blue screen with white text and can be caused by various issues.
Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to try and fix the issue so your computer runs smoothly again. This article will discuss troubleshooting and repairing the Blue Screen of Death on your Windows computer.
Disable Automatic Restart
Windows automatically restarts the computer when your computer encounters a blue screen error. To get more time to examine the details of a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) error or to confirm that it is a BSOD, you can turn off automatic restarts through the Control Panel.
1. Open the Start menu, type control, select, and open the Control panel.

2. Click on System.

3. In the right corner, click on Advanced system settings.

4. In the Advanced tab, click on Settings under the Startup and Recovery section.

5. Uncheck the Automatically restart box and click the OK button.

Run Windows Memory Diagnostic
The Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) is a common error that Windows users may encounter for various reasons, including computer memory problems. Faulty RAM can cause critical system errors, leading to BSOD errors, ultimately affecting the computer’s performance.
Windows Memory Diagnostic is a built-in tool in the Windows operating system that can detect and troubleshoot memory issues that could be causing BSOD errors. The tool runs diagnostic tests on the computer’s RAM (Random Access Memory) to detect any errors causing system instability, crashes, or other issues.
1. Open the Start menu and type memory.
2. Select Windows Memory Diagnostic app.

3. Select Restart now and check for the problems option.

4. After your computer restarts, open the Start menu and type Event.
5. Select Event viewer to find the result.
6. Click on Windows Logs > Security in the Event viewer window.
7. In the right pane, click on Find.

8. Type Memory Diagnostic and click the Find Next button.

9. You should see the Memory Dump File and Hexadecimal error code.

Check for Hard Drive Errors
If you are experiencing a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) error on your computer, it could be caused by a hardware failure. Checking for hardware errors is one of the most effective ways to fix these errors. This includes ensuring that all of your computer’s components are functioning correctly and that no issues exist with the connections between them.
By checking for hardware errors, you can help to ensure that your computer is running in optimal condition and can help to prevent further BSOD errors.
1. Press Win + E to open the File Explorer.

2. Click on This PC, right-click on your C: Drive, and select Properties.

3. Go to the Tools tab, click the Check button, and click Scan drive.

4. Follow on-screen instructions.
Update Device Driver
Updating device drivers can be a very effective way of resolving Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) problems. When new drivers are released, they often contain bug fixes and performance improvements that can directly address the issues causing the error. Updating the device drivers can avoid or resolve this issue, leading to a more stable computer system.
When updating device drivers, it is important to ensure the drivers are compatible with the hardware and operating system and that they are from a reliable source. Updating drivers can also help to keep device performance up to date and ensure better system compatibility.
1. Press Win + X and select Device manager.

2. Expand the Device driver that caused the problem.
3. Right-click on the driver and select Update driver.

Rollback Device Driver
Rolling back the device driver means restoring the driver to a previous version before the update was installed. This process can help eliminate any conflicts or compatibility issues introduced with the new driver update.
1. Press Win + X and select Device manager.

2. Expand the Device driver that is causing the problem.
3. Right-click on the driver and select Properties.
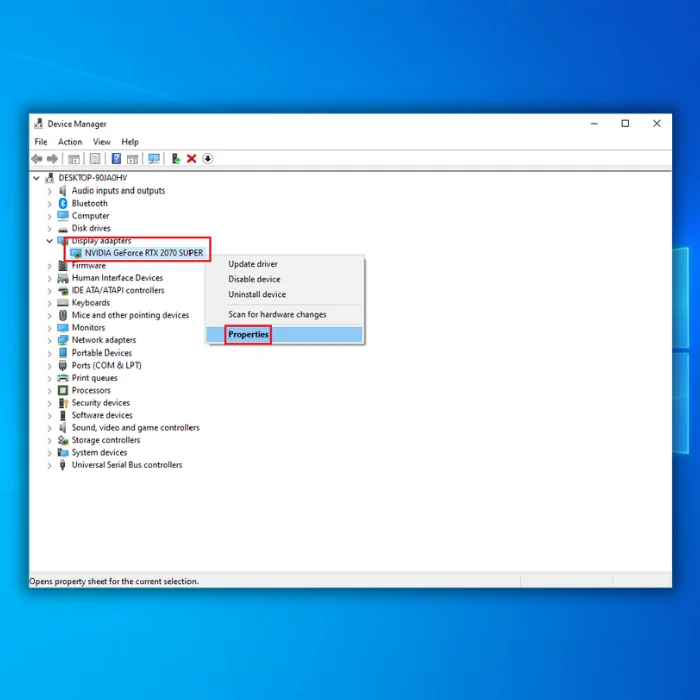
4. Go to the Driver tab and click the Roll Back Driver button.

Disable Device Driver
Disabling the device driver means preventing the operating system from using the driver for the hardware device in question. This process can help eliminate any conflicts or compatibility issues introduced with the driver, potentially resolving the BSOD error.
1. Press Win + X and select Device manager.

2. Expand the Device driver that is causing the problem.
3. Right-click on the driver and select Disable device.

Uninstall Device Drivers
BSOD occurs when your computer encounters an unexpected error from which it cannot recover. Various problems, including hardware issues, software conflicts, and driver issues, can cause it. Uninstalling the drivers associated with a device causing the issue can often help resolve the issue and prevent blue screens.
1. Press Win + X and select Device manager.
2. Expand the Device driver that is causing the problem.
3. Right-click on the driver and select Uninstall device.

Remove Non-essential Peripherals and New Hardware
Removing non-essential peripherals and new hardware from your computer can effectively fix the blue screen of death errors (BSOD). BSOD errors are often caused by the installation of new hardware that is incompatible with the computer or by other hardware or drivers that are not properly configured.
By removing hardware and peripherals that aren’t essential, you can reduce the number of possible conflicts and can even fix a BSOD error. Uninstalling any new hardware you recently installed can also help resolve the issue.
Change Defective or Incompatible Expansion Cards
Expansion cards are peripheral devices installed on a computer to enhance functionality. Examples of expansion cards include graphics cards, sound cards, and network adapters. In some cases, faulty or incompatible expansion cards can cause Blue Screen errors on Windows computers.
Conflicts may arise if the expansion card is incompatible with the computer’s motherboard or other hardware components, leading to system instability and crashes. Similarly, defective expansion cards may cause system errors that lead to BSoD errors.
Run SetupDiag
SetupDiag is a diagnostic tool provided by Microsoft to analyze and diagnose issues occurring during Windows 10 setup. It can be used to identify the cause of upgrade failures, errors, or other issues encountered during the Windows 10 upgrade process. The tool analyzes the log files created during the setup process and identifies the specific errors or issues that caused the installation failure or system crash.
1. Download and install SetupDiag from the Microsoft website.

2. Right-click on the SetupDiag.exe and select Run as an administrator.

3. Open the SetupDiagResults.log file.
Upon completing the steps, the default text editor will open the file containing the diagnostic results based on the established rules. In case of error detection, the logs will provide information to identify the reason for the device’s blue screen during the update.
Run SFC and DISM Tools
The “Blue Screen of Death” (BSOD) error on a Windows computer can be caused by various factors, including corrupted system files. In such cases, running the System File Checker (SFC) and Deployment Imaging and Servicing Management (DISM) tools can effectively troubleshoot to fix the BSOD error.
The SFC tool scans and repairs corrupted system files, while the DISM tool repairs the Windows system image and prepares the system for updates. Running both tools can help detect and fix any underlying issues with the system files, which can potentially resolve the BSOD error.
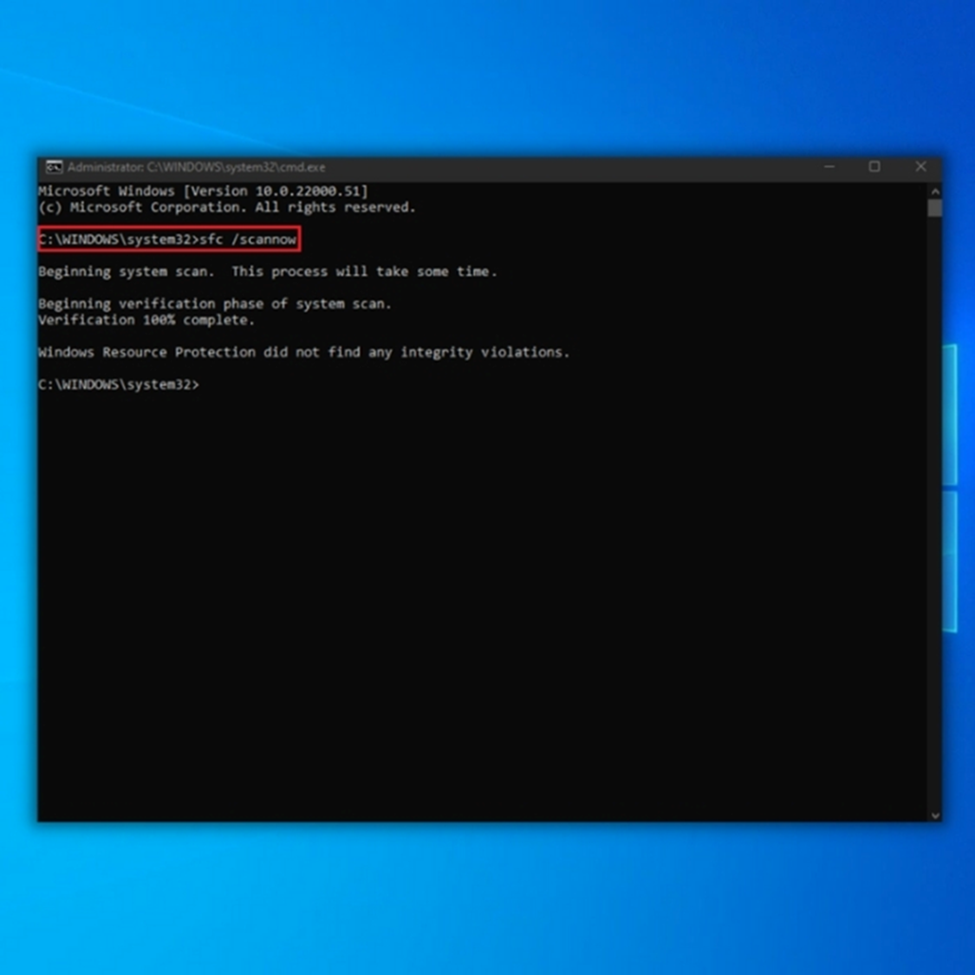
1. Open the Start menu and type cmd.
2. Select the Command prompt and Run it as an administrator.
3. In the command prompt window, type the following commands and press enter after each command:
SFC /scannow
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
How to Fix Blue Screen Error During Upgrade on Windows 10
While upgrading to a newer version of Windows 10, a blue screen occurs for various reasons, such as compatibility issues with outdated programs or security software, corrupted files in the current installation, or damaged installation media. In such instances, the setup may automatically revert the changes to the previous installation without providing any further explanation.
Uninstall Incompatible Software
One of the common causes of Blue Screen errors on Windows computers is incompatible software that may conflict with other system drivers or software components, causing critical errors.
If you are experiencing frequent BSODs, it may be due to an application or driver incompatible with your system. In such cases, uninstalling the problematic software can effectively fix the BSOD errors and restore system stability.
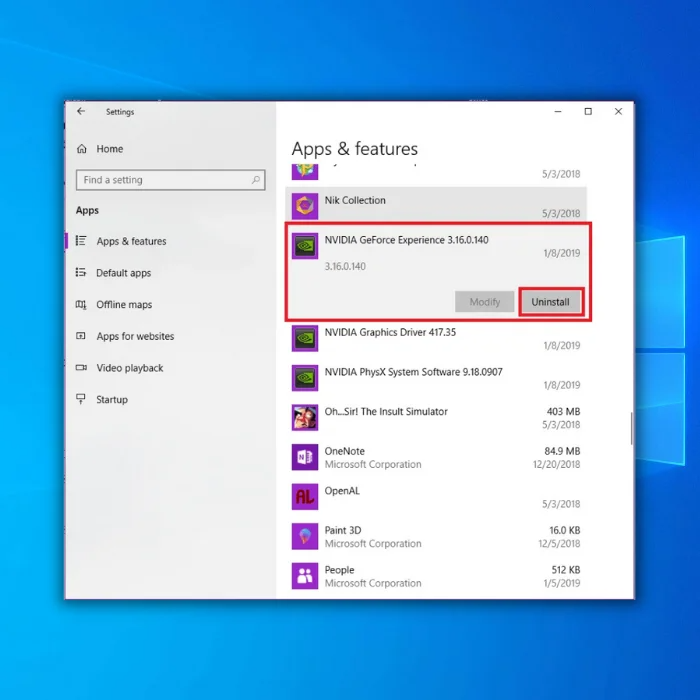
1. Press Win + I to open Windows Settings.
2. Click on Apps.
3. Go to Apps & Features, and search for the app that may have caused the problem
4. Click the Uninstall button.
Redownload Installation Files
Redownloading installation files may resolve blue screen errors during installation as the previously downloaded files could be corrupted or incomplete, resulting in errors during installation.
The likelihood of encountering errors due to corrupt or incomplete files is reduced by downloading fresh installation files. Additionally, it is recommended to ensure that the internet connection is stable and that there is enough storage space to download and install the files.
1. Open Windows Settings and click on System.
2. Go to the Storage tab and click on Temporary files.

3. Uncheck other selected options and check the Temporary Windows Installation files box.

4. Click the Remove files button.
Once you have finished the required steps, access the Windows Update settings and follow the prompts to attempt the computer upgrade process again.
Update Your PC Drivers
Drivers are software components that allow the operating system to communicate with hardware devices, such as graphics cards, sound cards, and network adapters. Outdated or corrupt drivers can cause compatibility issues or system conflicts, leading to blue-screen errors.
By updating drivers to the latest versions, users can potentially resolve blue screen errors caused by driver issues. The new drivers may include bug fixes, performance improvements, and compatibility updates that address known issues and prevent conflicts with other system components.
1. Open Windows Settings.
2. Click on Update & Security > Windows Updates > View optional updates.

3. Select the Driver updates and click the Download and install button.

Uninstall Recent System Updates
When users remove recent Windows updates, they essentially roll back their operating system to a previous state, eliminating any changes or modifications made by the updates. This can help isolate the problem and identify whether the recent updates caused the BSOD.
1. Open Settings > Update & Security.
2. Click on View update history.

3. Click on Uninstall updates.

4. Select the most recent Windows update and click the Uninstall button.

5. Restart your computer.
Perform A Clean Install
Performing a clean installation of Windows can fix blue screen errors by addressing software-related issues that could be causing the error. A blue screen error, also known as a “stop error,” occurs when the Windows operating system encounters a critical error that it cannot recover from, causing the system to crash and display a blue screen with error information.
A clean installation involves wiping the entire hard drive and installing a fresh copy of Windows without any existing files, applications, or settings. This process creates a clean slate for the operating system, eliminating any potential software conflicts or corrupt files that may be causing the blue screen errors.
1. Start your computer with Windows 10 installation media.
2. In the Windows setup screen, click Next > Install now.

3. Enter your product key, or you can skip it.
Ensuring that the edition selected matches the one the license activates is important. Using the incorrect edition can cause the product key to fail, potentially requiring reinstalling windows.
4. Select the Windows 10 edition and click the Next button.
5. Accept the License and terms and conditions.
6. Select Custom: Install Windows only (advanced) option.

7. Choose the partition with the current installation of Windows and click the Delete button.
8. Choose Drive 0 Unallocated Space and click the Next button.
9. Wait for the installation process to finish and boot your computer.
How to fix blue screen error without desktop access on Windows 10
Blue Screen of Death or simply blue screen error be a frustrating and confusing experience, particularly if you don’t have access to your desktop. Often, a blue screen error on Windows 10 can occur when a driver or system update has gone wrong, and the system crashes or shuts down unexpectedly. Fortunately, there are ways to fix a blue screen error without having access to the desktop.
Use System Restore from Advanced Startup
System Restore is a feature in Microsoft Windows that allows users to restore their computer’s system files earlier. It’s a useful tool for troubleshooting issues caused by software installations, driver updates, or other changes that may have caused system instability or errors.
By restoring the computer to its previous state, users can often resolve problems without fully reinstalling the operating system or resorting to other more time-consuming or complex troubleshooting methods.
1. Turn on and off your computer three times to enter the Advanced Startup screen.
2. Click on Troubleshoot.
3. Click on Advanced Options.

4. Select System Restore.

5. Select your local user account and confirm your password.
6. Click the Continue then the Next button.
7. Select your most recent Restore point and click the Scan for affected programs button.
8. Click the Next button, then Finish.
Using Safe Mode
Safe mode is a diagnostic mode of operation available in Microsoft Windows and other operating systems. It allows a computer to start up with only basic drivers and services without loading most software applications, services, and network connections that may be causing system problems.
1. Turn on and off your computer three times to enter Advanced Startup screen.
2. Click on Troubleshoot > Advanced Options
3. Select Startup Settings.

4. Click the Restart button.
5. Press the F4 key to select Enable safe mode after your computer restarts.

6. Now, you can follow the methods above to resolve blue screen errors.
In safe mode, Windows loads only the essential drivers.
Can Reinstalling Windows Help with the Blue Screen of the Death
Reinstalling Windows may help with the Blue Screen of Death, but it is not a guaranteed solution. Oftentimes, a BSOD occurs due to a software or hardware issue, and reinstalling Windows will not fix these underlying issues. It is, however, an easy way to solve problems related to corrupted files or drivers, as it will restore them to their original state.
While reinstalling can be effective in some cases, it is always recommended to try other methods first, such as restarting your computer or running diagnostic tests on the hardware components before attempting a full system reset. If all else fails, then taking this step may be your only option for resolving the issue.



![[FIXED] BSOD Windows 10 Error SYSTEM SERVICE EXCEPTION](https://cdn.techloris.com/app/uploads/2020/02/sse.jpg)
