![[Full Guide] How to Enter Recovery Mode Windows](https://cdn.techloris.com/app/uploads/2023/04/How-to-Enter-Recovery-Mode-Windows.png)
[Full Guide] How to Enter Recovery Mode Windows
Windows Recovery mode is a safe environment that allows users to troubleshoot and repair their Windows operating system. It provides access to several tools, such as System Restore and Automatic Repair, that can help diagnose and fix problems with the computer. The Windows recovery environment can also be used for other purposes, such as reinstalling the operating system or deleting corrupt files.
However, it’s also important to know the risks involved. For example, using certain tools in recovery mode can cause significant data loss or damage to your system beyond repair. Therefore, it is highly recommended that you have a reliable data backup before attempting any repairs in recovery mode.
Ensure Windows RE Is Enabled
Having Windows RE Enabled helps users access Windows Recovery Mode to troubleshoot their computer in case of a system failure or other issues. It enables advanced startup options, such as restoring the system from an earlier backup point or resetting the password.
When enabled, the first program runs when the computer boots up and allows you to launch tools like System Restore and Command Prompt before loading regular Windows programs.
To enable Windows Recovery Environment, follow these steps:
1. Open the Start menu and type cmd.
2. Select the Command prompt and run it as an administrator.
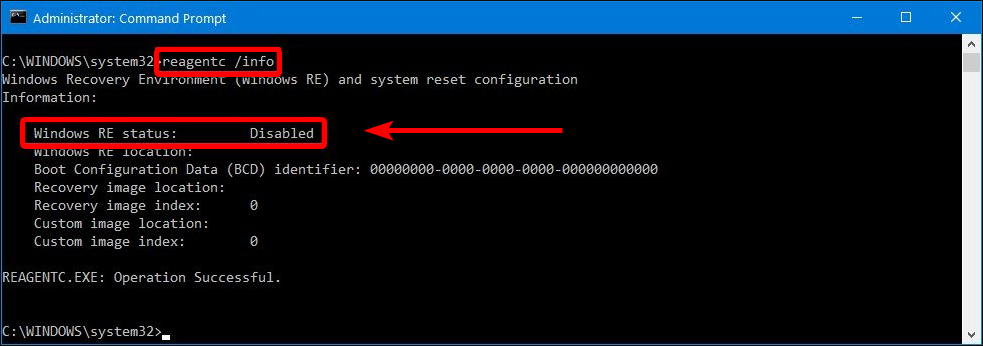
3. Type the following command to check if the WinRe is disabled and press Enter:
reagentc /info
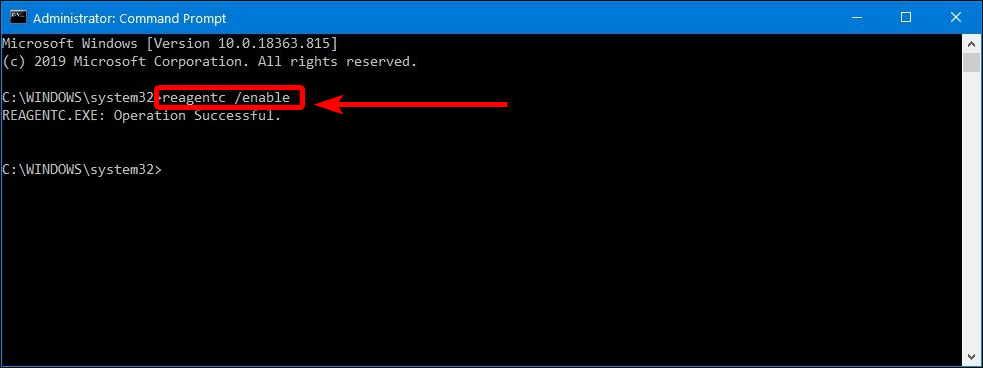
4. Next, type the following command to enable the recovery environment and press Enter:
reagentc /enable
Pressing F11 When the Computer Starts
1. Open or restart your computer.
2. Press the F11 key repeatedly while booting to enter recovery mode.
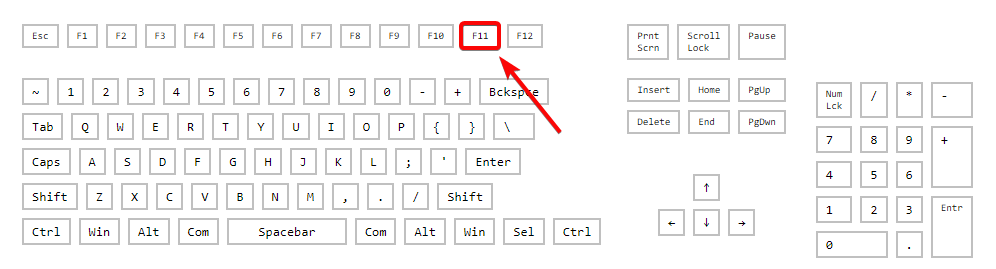
However, it depends on your computer’s manufacturer. Some may have the F9 or F12 keys by default.
Use the Restart Option of the Start Menu
The Restart Option of the Start Menu allows Windows users to quickly access advanced troubleshooting options, otherwise known as Windows Recovery Mode. This mode provides a range of tools and features that can be used to help resolve any issues or problems you may have with your system.
1. Press the Windows key and click on the Power button icon.
2. Hold and press the Shift key and click restart.
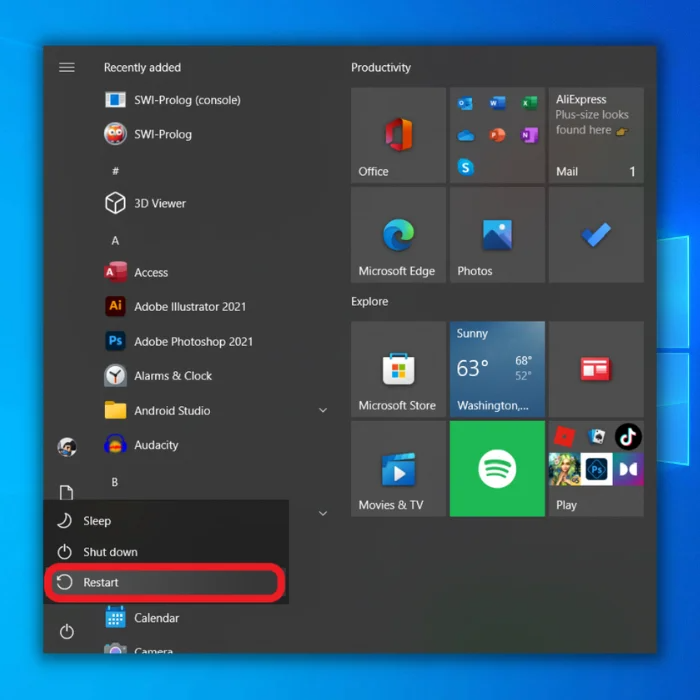
3. Click on Troubleshoot > Advanced options.
4. You can now access the recovery options listed on the screen.

Boot Via Settings App
Using the Settings app to boot into Windows Recovery Mode is a quick and easy way of accessing valuable troubleshooting options. You’ll need to open the Settings app on your computer to do this.
1. Press Win + I to open the Windows Settings app.
2. Click on Update & Security.
3. Go to the Recovery tab and click the Restart Now button under Advanced Startup.

4. Click on Troubleshoot > Advanced options.
Use Command Prompt to Enter WinRE
1. Open the Start menu and type cmd.
2. Select the Command prompt and run it as an administrator.
3. In the command prompt window, type the following command:
shutdown /r /o

4. You will see You’re about to signed out prompt; click Close.
5. Your PC will restart and will boot into recovery mode windows.
Boot Into Recovery Mode Using a Windows Bootable USB
Booting into Recovery Mode Using a Windows Bootable USB is an effective way to access the Windows Recovery Environment. This environment contains several tools that can be used to troubleshoot and repair problems with your system. You can access the Command Prompt, Advanced System Settings, and Startup Repair options by booting into this mode.
1. Create a bootable USB recovery media for Windows.
2. Turn off your PC and power it on.
3. Enter the BIOS and choose the USB flash drive.
4. In the Windows Setup screen, click on Repair your computer.

From the “Choose an Operating System” Screen
You can boot into the Windows recovery environment if you have another operating system.
You’ll see the Choose an operating system screen when you turn on your PC.
Click on Change defaults or choose other options > Choose other options.
You can now access WinRe.

Power off the PC by Force
The Windows Recovery Mode is a set of tools that can be used to repair or restore the operating system if it stops working correctly. It includes features like Startup Repair, System Restore, and File Recovery. Powering off the PC by force can help access these recovery options if Windows does not boot properly.
1. Turn your on and off your pc three times, and you will see Preparing automatic repair on your screen.
2. Click on See advanced repair options.

Boot via Lock Screen
1. Turn on your PC.
2. Click the Power button icon at the bottom right corner of the Login screen.
3. Hold and press the Shift key and click the restart option.

4. Click on Troubleshoot > Advanced options.
5. Select Startup settings > Restart.
6. Choose which boot options to enable safe mode after rebooting.

Access Recovery Mode Using System Configuration
1. Press Win + R to open the Run box.
2. Type in msconfig and press Enter.
3. Go to the Boot tab, check the Safe boot box, and click the Apply button.
4. Restart your PC to apply the new settings.

5. Windows will now boot into a safe recovery environment.
Boot via Windows Powershell
1. Press Win + X and select Windows PowerShell (Admin).

2. Type the following command and press enter:
shutdown /r /o
3. Windows should boot into Recovery Mode Windows in 30 seconds.
4. If you encounter problems, you can re-run the command with extra parameters.
shutdown /r /o /f /t 0
5. This command will force close all programs and boot the system instantly.
Use the F8 Key
1. First, you need to enable the F8 key.
2. Open the Command prompt, type bcdedit /set {default} bootmenupolicy legacy, then press Enter.

3. Restart your PC and press the F8 key repeatedly.
What Are The Recovery Tools?
System Restore
This built-in feature in Windows operating systems allows users to restore their computer to an earlier state when it functions appropriately using a restore point. System Restore does not affect personal files but can remove installed programs and updates. If you install a large update and find yourself aggravated with the new features, you can use the system restore to back up your operating system to an earlier date with previous features.
System Image Recovery
System Image Recovery is a feature in Windows operating systems that allows users to restore their computer to a previous state using a system image backup. A system image is a complete copy of a computer’s hard drive, including the operating system, installed programs, system settings, and personal files. System Image Recovery can be used in case of a system failure, such as a corrupted or damaged operating system, hardware failure, or a virus attack.
Startup Repair
This tool is designed to automatically fix common issues that prevent Windows from starting up, such as corrupt system files or problems with the boot configuration.
Command Prompt
This tool provides a command-line interface that allows users to perform various system-level tasks, such as repairing corrupt files, troubleshooting network issues, and resetting passwords.
Automatic Repair
This tool is designed to automatically detect and fix startup issues that prevent Windows from loading properly.
Reset This PC
This tool allows users to reset their computer to its factory settings while keeping their files or removing everything, depending on their choice.
Startup Settings
This tool provides advanced options for troubleshooting startup issues, such as booting in safe mode, enabling debugging mode, or disabling driver signature enforcement.
What Does the Recovery Mode Do?
Recovery mode is a feature built into many electronic devices, including computers, smartphones, and tablets, that allows users to troubleshoot and fix various problems that may be preventing the device from functioning properly. In recovery mode, the device typically boots into a special mode that provides limited functions and options designed to help users diagnose and resolve issues.
Some of the common functions that can be performed in recovery mode include:
- Rebooting the device: This is the simplest function that can be performed in recovery mode. If the device is frozen or unresponsive, recovery mode can be used to restart the device.
- Wiping data: Sometimes, a device may have a software issue preventing it from functioning correctly. In such cases, wiping the device’s data may be necessary to fix the problem. This function is typically used as a last resort since it erases all data on the device.
- Installing system updates: Recovery mode can also be used to install system updates on the device. This function is useful if the device has issues with a particular update or is not running the latest operating system version.
- Factory resetting the device: If none of the above options work, factory resetting the device may be necessary. This function erases all data on the device and returns it to its original factory settings.
Recovery mode is a helpful tool to help users troubleshoot and fix various device issues. However, it should be used cautiously since some functions, such as wiping data and factory resetting, can result in losing important information.
Unlocking the Power of Recovery Mode: A Comprehensive Guide
In this comprehensive guide, we have delved into the intricacies of entering Recovery Mode in Windows, equipping you with the knowledge and tools to troubleshoot and resolve various system issues. Following the step-by-step instructions, you can confidently navigate the Recovery Mode interface and utilize its powerful features to repair your Windows system, restore functionality, and recover valuable data. Whether you are encountering startup problems, system errors, or need to revert to a previous system state, this guide has provided you with the necessary insights to leverage Recovery Mode effectively. With the ability to access advanced troubleshooting options, perform system repairs, and reset your PC, you can overcome obstacles and bring your Windows system back to a stable and functional state. Remember, Recovery Mode is a valuable ally in your Windows troubleshooting journey, so keep this guide handy for future reference and harness the power of Recovery Mode to reclaim control over your Windows experience.
Frequently Asked Questions About Recovery Mode Windows
Why Can’t I Update Windows Recovery Environment?
The Windows Recovery Environment (Windows RE) is a set of tools to help you troubleshoot and repair your computer when it fails to start correctly. However, sometimes users may encounter issues while updating their Windows RE. This can happen for various reasons, such as incorrect registry settings, missing files, or system corruption.
Does Windows Recovery Environment Help With System Restore?
Yes, Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) can help with System Restore. System Restore is a Windows feature that allows you to roll back your computer system to a previous state if something goes wrong or stops working properly. WinRE provides tools and options to create restore points and perform system restores more easily than the standard Windows GUI.
Can I Update Windows Startup Settings?
Yes, you can update your Windows startup settings. This allows you to choose which programs and services will start automatically when you boot up your device. To do this, go to the Task Manager in the Start Menu, select the Startup tab, and click on the program or service you’d like to adjust.
Can I Disable Recovery Mode in Windows 10?
Yes, you can disable Recovery Mode in Windows 10. There are two ways to do this: by modifying the system registry or using a third-party tool. Modifying the system registry is a more technical approach and requires some knowledge of editing the registry, and it involves editing registry values such as DisableRecoveryMode, AutoReboot, and DisableAutomaticRestart.
Do I Need a Bootable USB Drive for Windows Recovery Mode?
Yes, you will need a bootable USB drive for Windows recovery mode. This is because the Windows installation files are too large to fit on a regular CD or DVD and, thus, must be stored on a larger storage device such as a USB flash drive or hard drive. To create a bootable USB drive for Windows recovery mode, you must use a utility such as Windows USB/DVD Download Tool, Rufus, or UNetbootin.
Will Windows Recovery Mode Delete Installation Media?
No, Windows Recovery Mode won’t delete installation media. When you enter this mode, it will give you access to several troubleshooting and recovery tools that can help fix various issues with your system. However, it cannot delete files or folders from your computer, including any installation media such as CDs or USB drives.
Can I Run Recovery Mode With Out the Windows Server?
No, you cannot run recovery mode without Windows Server. Recovery mode is a Windows Server operating system feature that allows users to restore their computer to an earlier point in time or roll back unwanted changes. You must install and activate your computer’s Windows Server operating system to access this functionality.
What Is External Media on Windows?
External media is an external storage device that can store and transfer data from one computer system to another. It can be a removable physical storage device (such as a USB flash drive, optical disc, or floppy disk) or a virtual storage service accessed over the internet (such as cloud storage).
Is a Hard Reboot Secure for Recovery Mode on Windows?
The answer to this question depends on the type of recovery mode utilized. Generally speaking, hard reboots are secure for basic recovery modes that restore lost data. However, more advanced recovery modes can be vulnerable to hard reboot and may cause serious damage or security risks if mismanaged.

![[Full Usage Guide] Windows 10 Recovery Mode Activation](https://cdn.techloris.com/app/uploads/2023/03/activate-recovery-mode-windows-10.png)


![[Guide] How To Launch Windows 10 Safe Mode From Boot](https://cdn.techloris.com/app/uploads/2023/01/launch-windows-10-in-safemode.png)